Comprehensive Guide To Java
Introduction
Java is one of the most popular programming languages globally, known for its versatility, platform independence, and robustness. This guide provides a deep dive into Java programming, covering essential concepts and tools that enable developers to build everything from small applications to large-scale enterprise systems. It emphasizes Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) principles, Java frameworks, and best practices to help both beginners and experienced developers become proficient in Java.
The guide also explores advanced Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) concepts and frameworks such as Hibernate and Spring, which are critical for building scalable, high-performance enterprise applications. Whether you're new to Java or looking to expand your skills, this guide provides the foundation and advanced knowledge needed to succeed in a Java-based development environment.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Java
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Java Collections Framework
- Exception Handling
- Java Enterprise Essentials
- JDBC, Servlets, and JSP
- Hibernate and ORM (Object-Relational Mapping)
- Spring Framework
- Spring Boot
- Microservices with Java
Java Programming Concepts
Introduction to Java
Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language designed to be platform-independent. With the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Java code can run on any system with the JVM installed, providing "write once, run anywhere" capability. This section covers the fundamentals of Java syntax, data types, operators, and control structures. It provides a foundational understanding of Java programming, helping beginners get started with core concepts like classes, objects, methods, and packages.

Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Java is fundamentally an object-oriented programming language, which means it leverages the four principles of OOP: Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance, and Polymorphism. This section introduces OOP principles and demonstrates how to implement them in Java. By understanding these concepts, developers can create modular, reusable, and organized code structures, improving the maintainability and scalability of applications.
Java Collections Framework
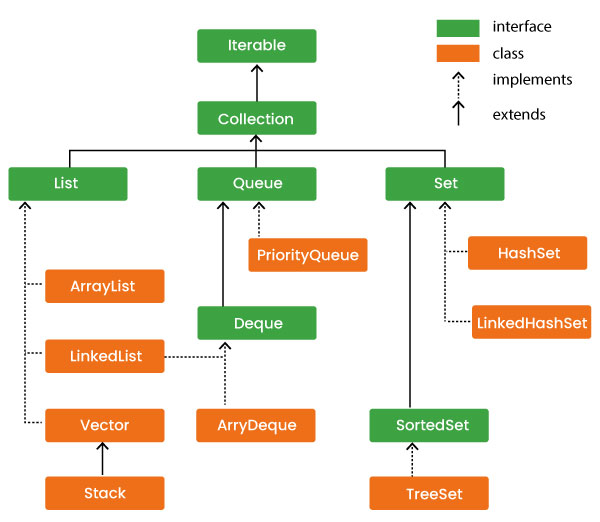
The Java Collections Framework provides a set of data structures and algorithms to store, retrieve, and manipulate collections of data. This includes classes like ArrayList, HashMap, LinkedList, and HashSet. Mastering these classes allows developers to handle complex data operations efficiently, which is crucial for building scalable applications. This section covers collections in detail, from basic usage to more advanced features like sorting, filtering, and concurrency.
Exception Handling
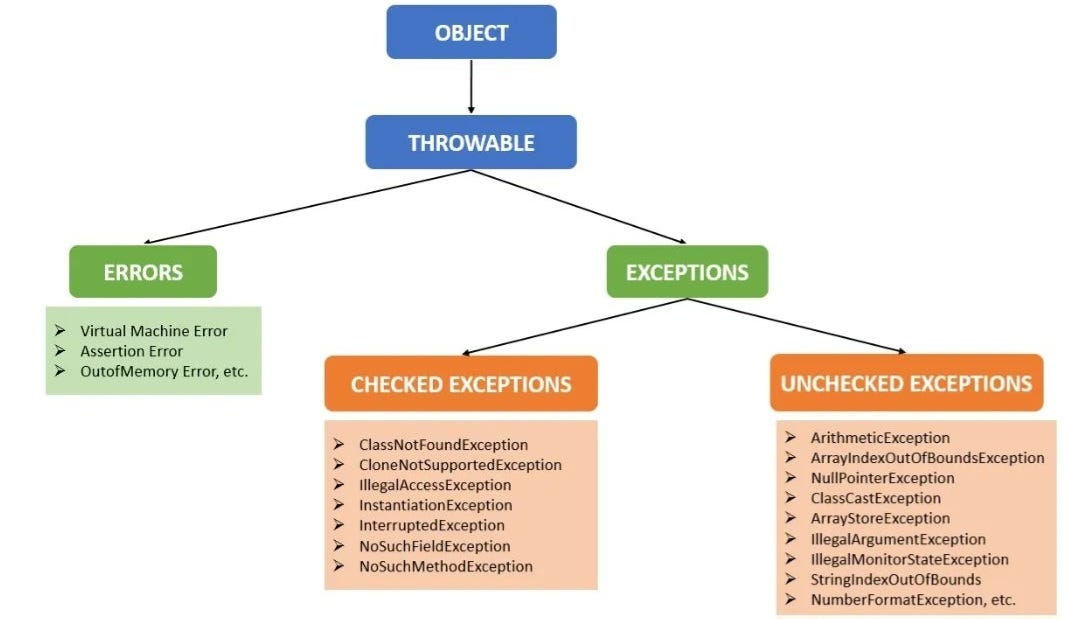
Exception handling is a critical aspect of Java programming, enabling developers to manage runtime errors gracefully. This section covers the basics of try-catch blocks, throws, throw, and finally. Understanding how to handle exceptions properly helps in creating robust and fault-tolerant applications. Developers will learn best practices for managing checked and unchecked exceptions, ensuring code reliability and stability.
Java Enterprise Essentials
Java EE (Java Enterprise Edition) provides a platform for building large-scale, distributed, and multi-tiered enterprise applications. This section introduces essential concepts in Java EE, such as dependency injection, EJB (Enterprise JavaBeans), and JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface). It prepares developers to work in enterprise environments where Java EE applications are widely used for business-critical systems.

JDBC, Servlets, and JSP
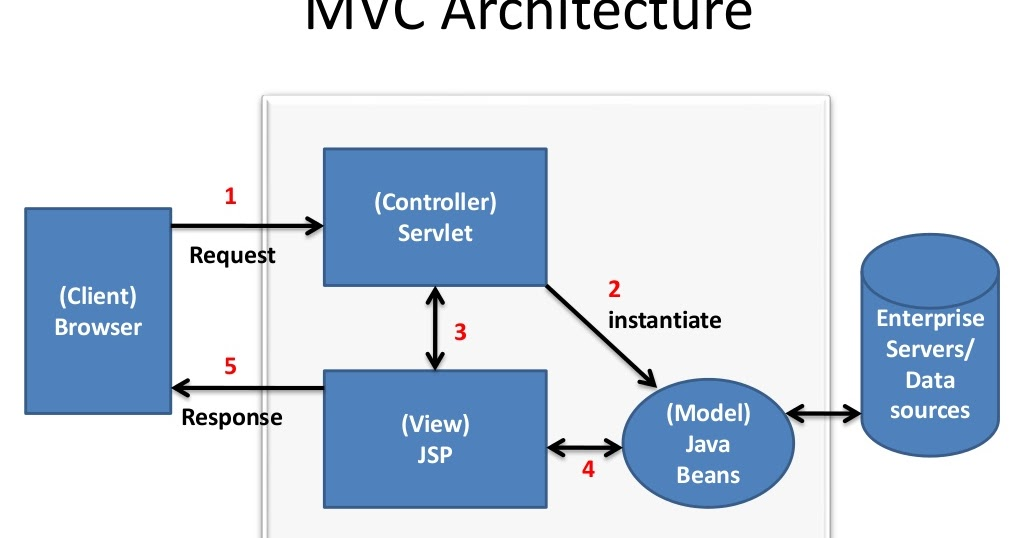
JDBC (Java Database Connectivity), Servlets, and JSP (JavaServer Pages) are fundamental for building web applications in Java. JDBC allows Java applications to interact with databases, enabling CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. Servlets and JSP facilitate dynamic content generation for web applications. This section covers how to connect to databases, build backend logic, and generate dynamic HTML pages using Java, laying the groundwork for full-stack Java development.
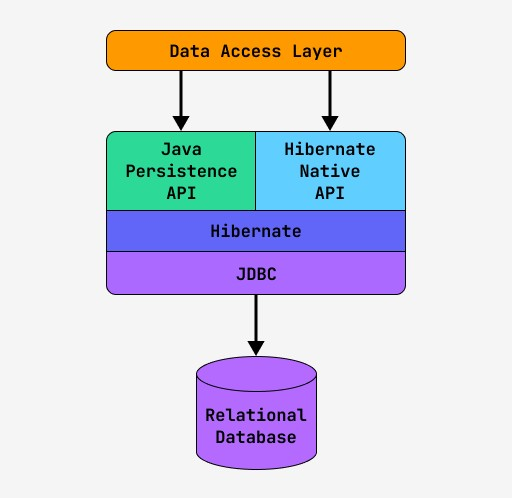
Hibernate and ORM (Object-Relational Mapping)
Hibernate is a popular ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework that simplifies database operations by mapping Java classes to database tables. This section introduces Hibernate basics, including mapping entities, CRUD operations, and querying databases using HQL (Hibernate Query Language). Hibernate eliminates the need for complex SQL queries, allowing developers to interact with databases in a more object-oriented manner. Understanding Hibernate is crucial for building data-driven Java applications efficiently.
Spring Framework
The Spring Framework is a comprehensive framework for building enterprise Java applications. It provides tools for dependency injection, transaction management, and aspect-oriented programming (AOP), making it easier to create loosely coupled, maintainable code. This section covers core Spring components such as Spring Core, Spring MVC, and Spring Data JPA, preparing developers to build modular, scalable applications with Spring.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is an extension of the Spring Framework that simplifies the setup and development of production-ready applications. With its opinionated approach, Spring Boot minimizes the need for boilerplate configuration, allowing developers to focus on application logic. This section covers building RESTful APIs, configuring Spring Boot, and deploying Spring Boot applications, making it an essential tool for rapid application development in Java.

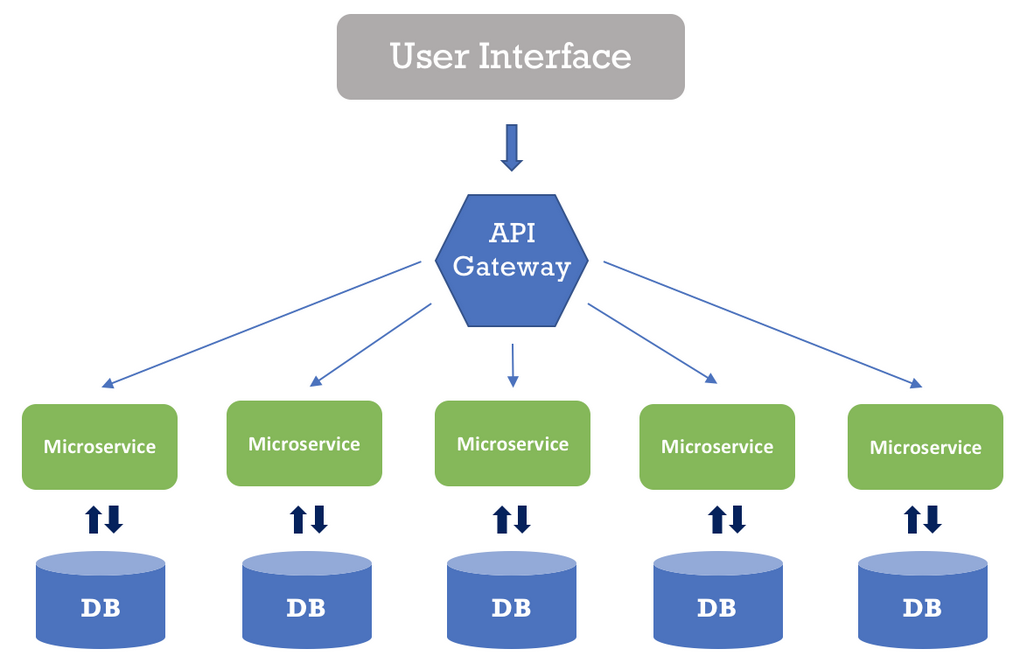
Microservices with Java
Microservices is an architectural style where applications are composed of small, loosely coupled services that can be independently deployed and scaled. This section explores building microservices using Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, covering topics like service discovery, load balancing, and API Gateway. Microservices are essential for modern application development, and Java, combined with Spring Boot, provides a robust framework for implementing them.
Conclusion
ava remains a vital language in the software industry due to its platform independence, performance, and versatility. From web applications to Android apps, Java's rich ecosystem supports a wide range of applications. For beginners, mastering core concepts like OOP, Collections, and Exception Handling builds a solid foundation. For advanced developers, understanding frameworks like Spring, Hibernate, and microservices architecture enables the development of robust and scalable enterprise applications.