Comprehensive Guide To AWS Data Engineering
Introduction
In today's data-centric world, organizations generate vast amounts of data every second. The ability to effectively store, process, and analyze this data is crucial for making informed business decisions. Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers a comprehensive suite of data engineering services designed to handle big data workloads efficiently and cost-effectively.
This guide provides a beginner-friendly overview of various AWS data engineering services, how they build upon traditional data systems like Hadoop, and how they integrate to create robust data solutions in the cloud. Whether you're new to data engineering or transitioning from on-premises solutions, this guide will help you understand the core AWS services and how to leverage them.
Table of Contents
Understanding Big Data and Data Engineering
Big Data refers to datasets that are so large or complex that traditional data processing applications are inadequate to handle them. Big data challenges include capturing data, data storage, data analysis, search, sharing, updating, and information privacy.
Data Engineering involves designing, building, and managing systems and infrastructure for collecting, storing, and analyzing big data. Data engineers ensure that data flows smoothly and securely between servers and applications.
Introduction to Hadoop and HDFS
What is Hadoop?
Apache Hadoop is an open-source framework designed to process and store large datasets across clusters of computers using simple programming models. It enables distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using MapReduce programming models.
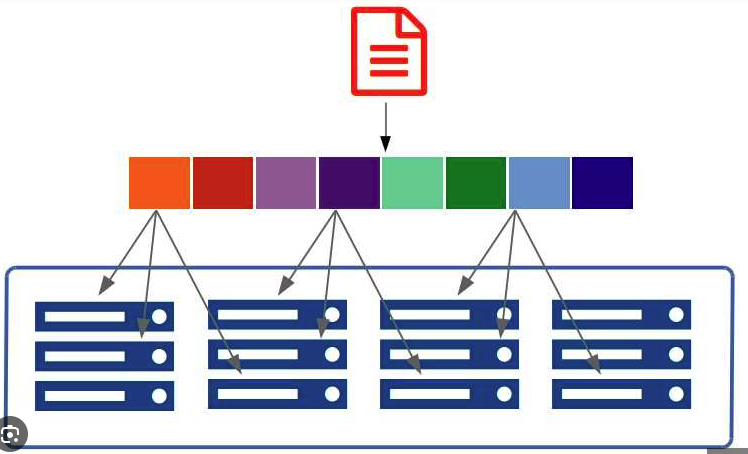
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS)
HDFS is the primary data storage system used by Hadoop applications. It is designed to scale to petabytes of data and can be run on commodity hardware.
How HDFS Works
- Data Blocks: Large files are split into blocks (default size is 128 MB or 256 MB).
- Data Distribution:
- Each block is stored across different nodes in a Hadoop cluster.
- Blocks are replicated for fault tolerance (default replication factor is 3).
- Parallel Processing:
- Jobs are divided into tasks that are processed in parallel on different nodes.
- Utilizes MapReduce for processing.
Example:
- A 600 MB file is split into 5 blocks of 128 MB each.
- Blocks are distributed across multiple nodes in the cluster.
- A data processing job runs tasks on each block in parallel, reducing overall processing time.
Diagram: HDFS Data Distribution